
Differences Between Residential and Commercial Roofing
Are you confused about the differences between residential and commercial roofing? Learn more about the benefits and considerations of each …
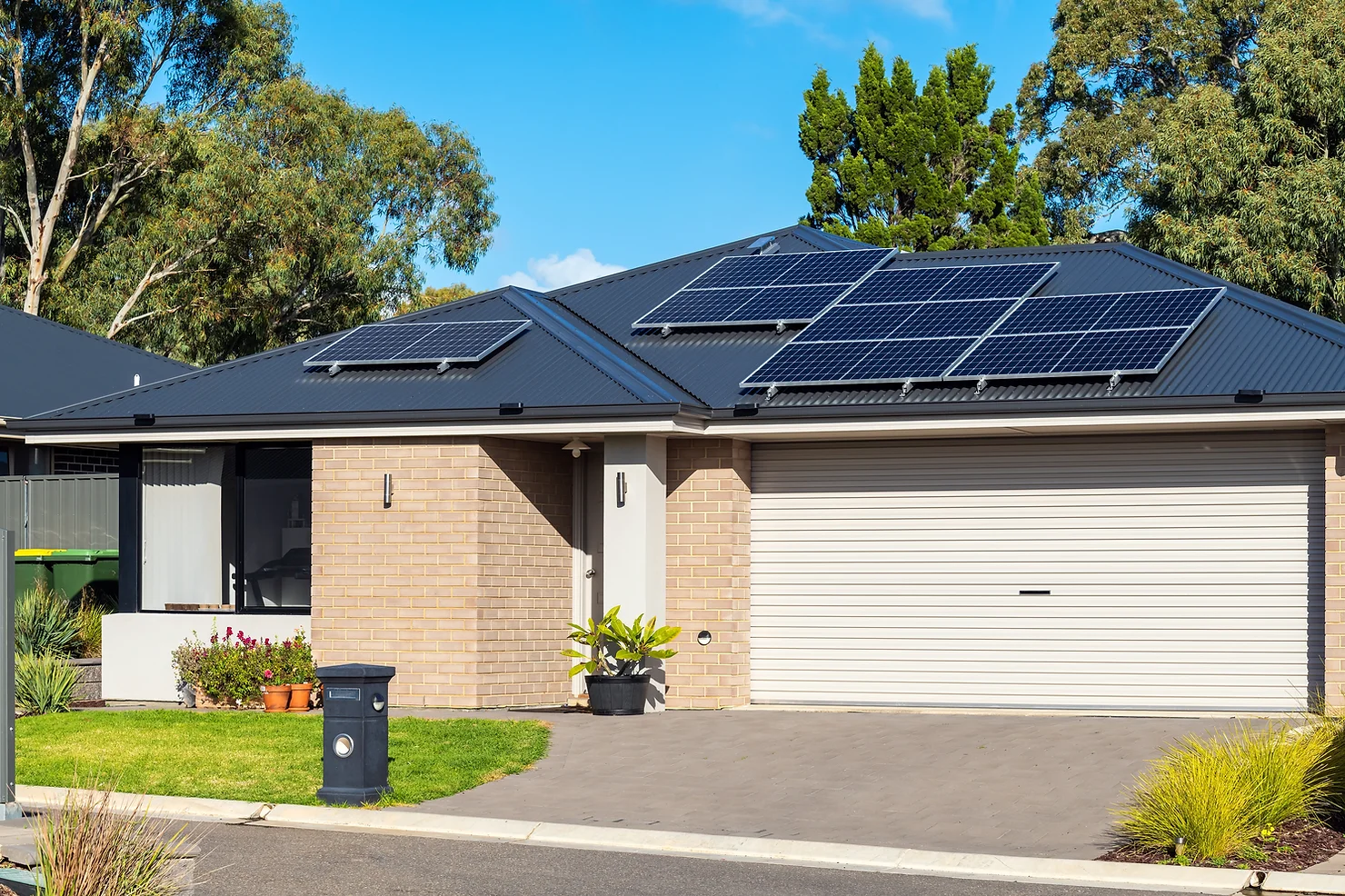

Making the transition to solar energy is a significant and potentially rewarding decision, but it requires careful planning and analysis. Lifetime Quality Solar is here to support you on this journey, providing a thorough roof inspection before proceeding with any solar panel installation. This article provides an in-depth guide to understanding the different types of solar panels available on the market, their pros and cons, and how to make the best decision for your home or business.
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices designed to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. They are made up of individual solar cells, which are typically composed of layers of silicon, boron, and phosphorus. The interaction of these elements under sunlight results in a directional current which is harnessed as usable power.
There are primarily three types of solar panels available in the market: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels.
Constructed from a single pure silicon crystal, monocrystalline panels are known for their high efficiency and performance. However, they are also the most expensive due to the complex and resource-intensive manufacturing process.
Polycrystalline panels, on the other hand, are made up of multiple silicon crystals. They are less expensive and less efficient than their monocrystalline counterparts.
The third type, thin-film panels, are made from a thin layer of semiconductor material. They are the least expensive and least efficient among the three but offer flexibility and lightweight advantages.
Each type of solar panel offers specific advantages that make them suitable for different applications and requirements.
Monocrystalline panels provide high efficiency, making them ideal for properties with high electricity consumption. They are also space-efficient, durable, and aesthetically pleasing with their characteristic black color.
Polycrystalline panels, with their lower costs and versatility, are a cost-effective solution for many homeowners. They offer reliability and a long lifespan, making them a sound investment.
Thin-film panels, due to their flexible and lightweight nature, are excellent for non-traditional installations, such as on curved surfaces or lightweight structures.
Despite their advantages, each type of solar panel also comes with its own set of disadvantages.
The high costs of monocrystalline panels can be a deterrent for some, especially for large-scale installations.
Polycrystalline panels, on the other hand, are less efficient and require more surface area for installation, which may not be suitable for smaller properties.
While thin-film panels are flexible and lightweight, they degrade more quickly than other types, which could lead to a shorter lifespan in locations with extreme weather conditions.
When budgeting for a solar panel installation, it's important to consider the costs associated with each type of panel.
Monocrystalline panels are the most expensive option, costing between $1 and $1.50 per watt.
Polycrystalline panels are more budget-friendly, ranging from $0.90 to $1 per watt.
Thin-film panels fall in the middle of these estimates, costing about $1 to $1.20 per watt.
The visual appeal of solar panels can be a deciding factor for some homeowners. Monocrystalline panels have black cells and blend well with traditional roofing materials. Polycrystalline panels appear bluish due to the different crystal structure. Thin-film panels are flexible and can be customized into various shapes, making them an aesthetically appealing option for unique architectural designs.
Efficiency is a critical factor when choosing solar panels. Monocrystalline panels lead the pack with efficiency rates over 20%. Polycrystalline panels provide efficiency between 15 to 17%, while thin-film panels usually offer around 11% efficiency.
The longevity of your solar panels is a crucial consideration. Both monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels have lifespans of over 25 years. Thin-film panels, due to their composition, may have a slightly shorter lifespan, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions.
Your choice of solar panel should align with your property's requirements and your project's goals. Monocrystalline panels are ideal for those looking to maximize electricity production in limited spaces, while polycrystalline panels are a cost-effective solution for properties with ample space. Thin-film panels are well-suited for unconventional installations or lightweight structures.
At Lifetime Quality Solar, we conduct a thorough roof inspection before any solar panel installation to ensure the best possible outcome. We are committed to helping you make an informed decision, offering a lifetime warranty for peace of mind. Our team of experts is ready to guide you through the process, ensuring a smooth transition to solar power.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of solar panels and their characteristics can help you make a more informed decision. Whether you opt for monocrystalline, polycrystalline, or thin-film panels, each type offers unique advantages that can meet your specific solar energy needs.